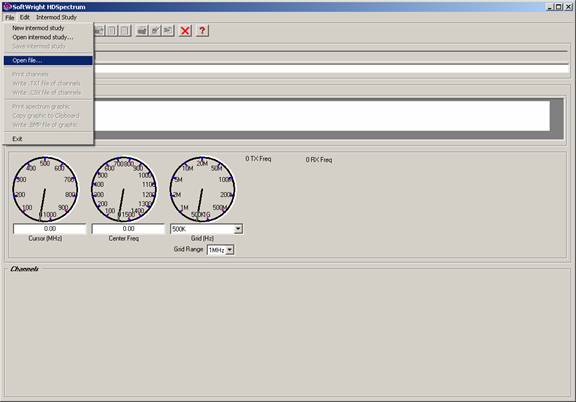
File Formats in HDSpectrum™
Q: How do I use frequency information I have in another file format with HDSpectrum?
A: If you can modify the file format of your file you can read it directly into HDSpectrum.
(Note that all values and settings in this article are for illustration purposes only. You should determine the appropriate settings for your application using good engineering judgment.)
You can use the import function in TAP 6.0.2172 or later to read an Excel spreadsheet file directly. For earlier versions of TAP you can use the procedures described below.
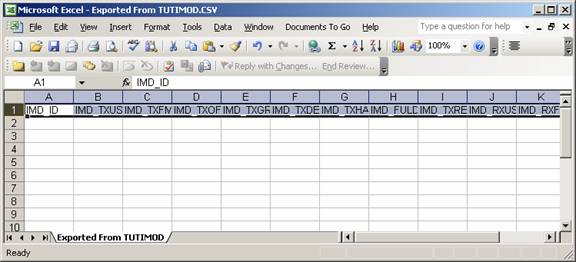
If you want to create a new intermod database for an intermod study in HDSpectrum, and you want to do all the editing in HDSpectrum itself, you can create a new study as described in New Intermod Database in HDSpectrum. An alternative, if you want to create a new file to edit in Microsoft Excel, you can open an existing intermod database (such as the INTERMOD\TutImod.DBF file supplied for the TAP demo and tutorials):

Select the file:
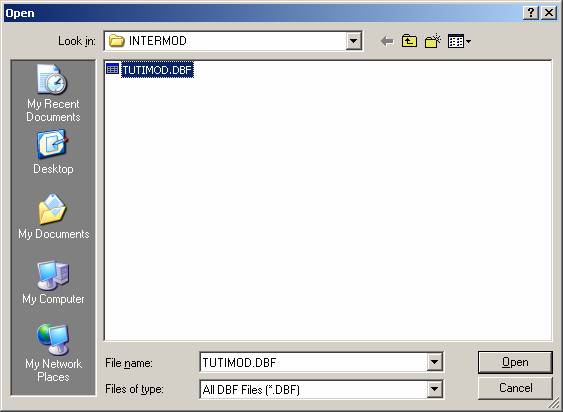
Then use the HDSPectrum “Export to CSV File button ![]() to export the
file as describe in Export from HDSpectrum.
to export the
file as describe in Export from HDSpectrum.
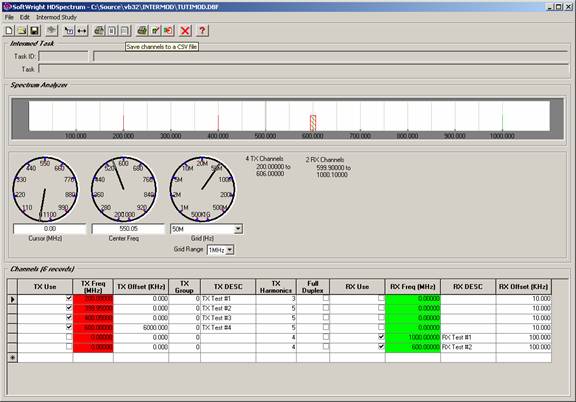
Then you can open that file in Excel and delete the existing records and add your own.
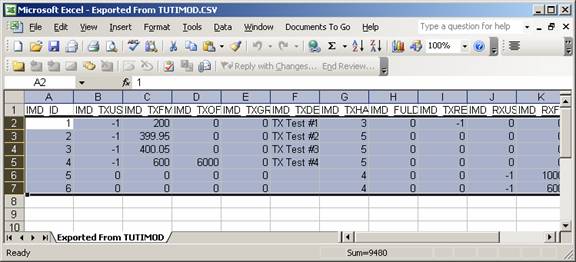
Be sure not to delete the first row which defines the database file names expected by HDSpectrum.
After making the desired edits you can open the file in HDSpectrum as described below.
HDSpectrum reads dBaseIV database (.dbf) files containing the fields described in the article on Database Fields in HDSpectrum. You can make a copy of your file (such as an Excel (.xls) or comma-delimited ASCII (.csv) file, then modify the copy to conform to the HDSpectrum data specification
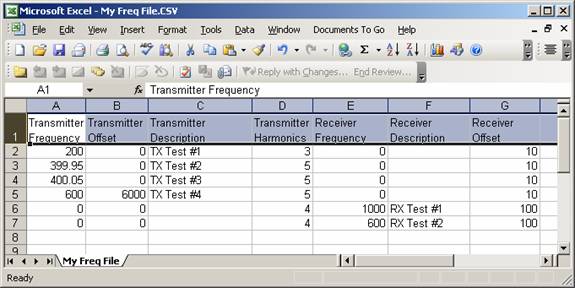
For example, suppose you have a comma-delimited (or Excel) file named “My Freq File.CSV” with data as shown below in Microsoft Excel:
Rename the column headers to match the database field names expected by HDSpectrum:
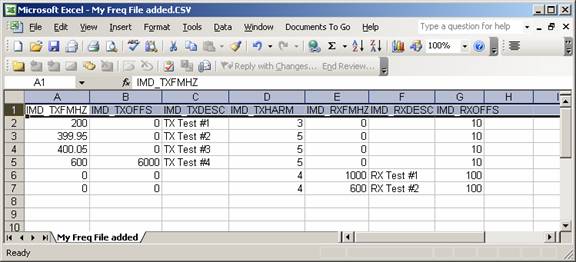
Be sure the units for the values for transmitter and receiver center frequencies are in megahertz, and the offset frequencies are in kilohertz. Also note that the offset values are the frequency range above and below the center frequency and not the bandwidth that includes both sides of the center frequency.
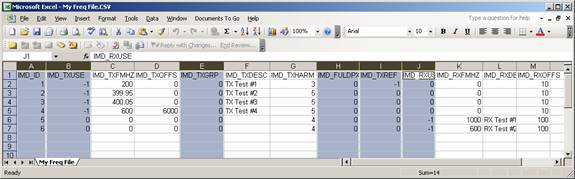
Use the “Insert|Columns” menu in Excel to add columns required in the HDSpectrum format that are not already in your file and enter the header names. Enter the appropriate values for each record in each column:
Use the “File|Save As” menu in Excel to save the file and select the dBaseIV (.dbf) file type:
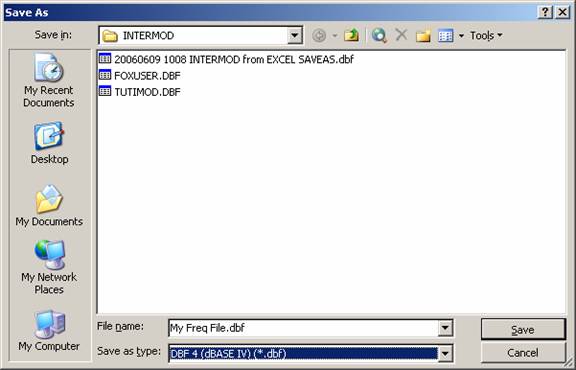
You will be prompted to save the file in the new format.
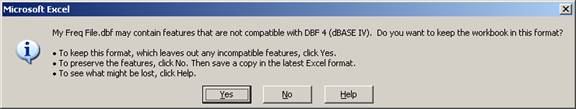
Since the HDSpectrum and TAP intermod database format is a simple, “flat” database, there is no concern about the warnings about “incompatible features.’ Click the Yes button.
Depending on your Excel configuration settings, you may be prompted again to save the file. Click the Yes button:
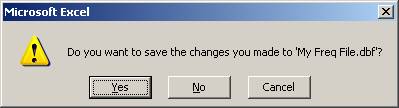
When you close the file, you may see the “incompatible features” warning again. If so, just click the Yes button again.
Now you can use the “File|Open File” menu in HDSpectrum to open the file:
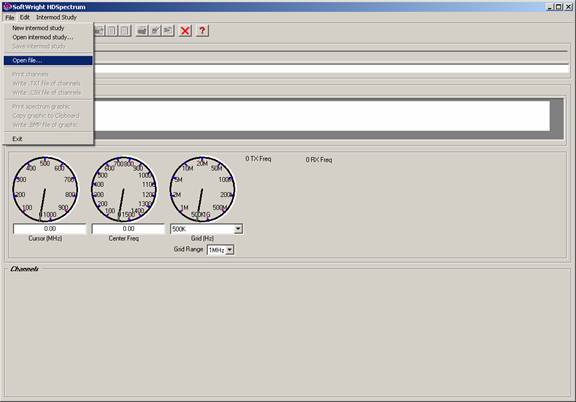
Select the file you created:
The information from your original “My Freq File.CSV” file, along with information you added, is displayed in HDSpectrum:
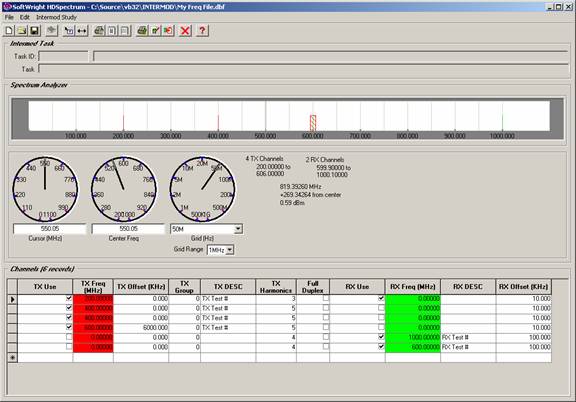
You can manipulate and edit the values as described in the article on HDSpectrum Graphic View.
You can use the database to create a new intermod study as described in Intermod Setup in HDSpectrum.
Copyright 2006 by SoftWright LLC