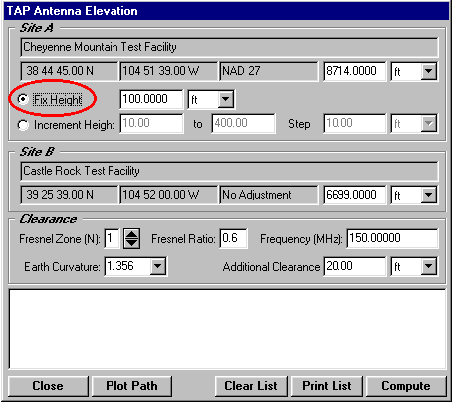
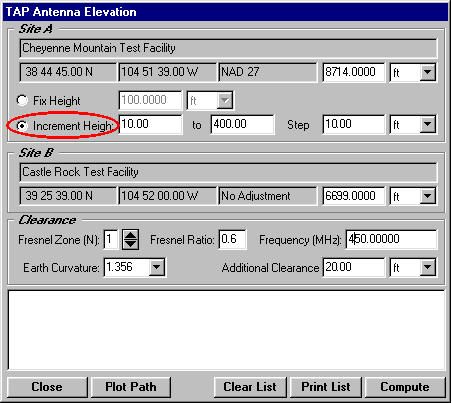
Q: How can I use TAP to determine the antenna height I need for a point-to-point path?
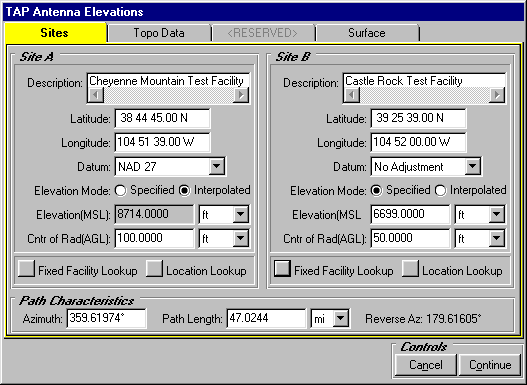
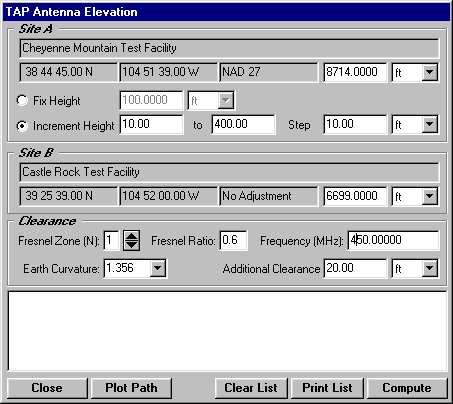
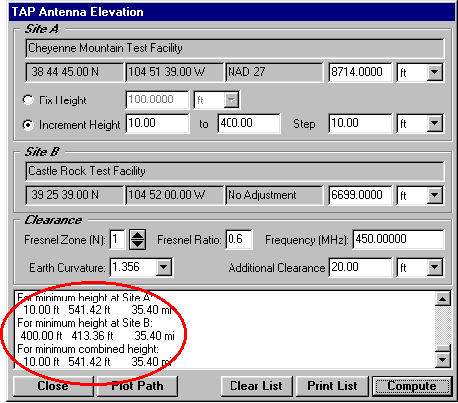
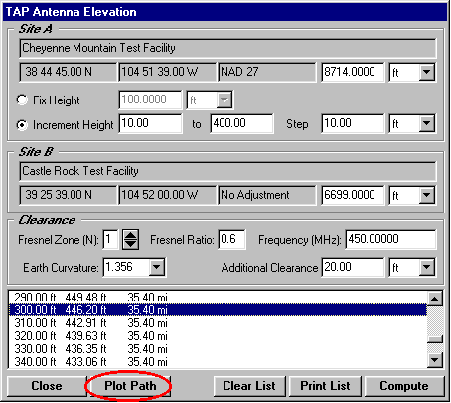
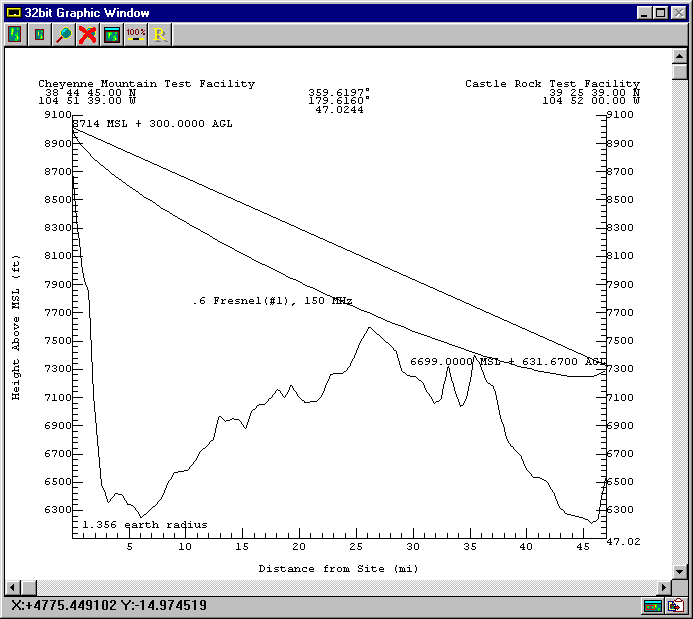
A: SoftWright’s Terrain Analysis Package (TAP)Ô (Version 4.00.201 and later, 32-bit version only) includes the optional Antenna Elevation module, found in the Path menu. This program allows you to specify the coordinates of the two end-points of a path, and the desired antenna elevation(s) on one end. You can specify the desired frequency and Fresnel zone clearance, as well as an additional "buffer" clearance value. (For example, you could specify .6 of the first Fresnel zone at 450 MHz, plus 20 feet.) The program will compute the antenna elevation on the other end of the path necessary to achieve your specifications.
(Note that TAP users with Version 5.0.1056 and later can use the HDPath interface to draw profiles and to compute antenna elevation values.)






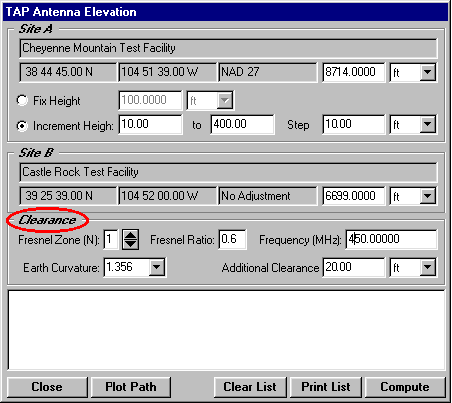
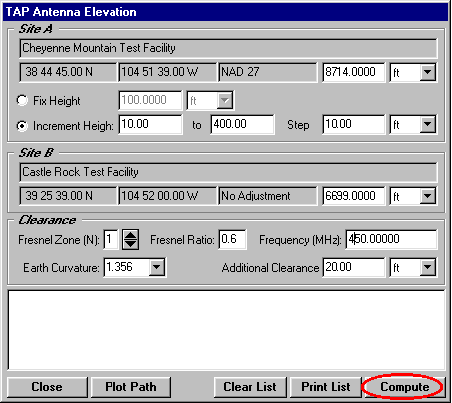
Copyright 1999 by SoftWright LLC